|
|
|
|
Liquids and Solids
Copyright
D. Herrick |
 |
| |
20 Questions from past exams.
Practice for speed. Aim
for 1 minute per problem.
|
|
| 1. |
Which
compound has the higher boiling point?
|
|
| A) |
CH3-CH2-CH3 |
B) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 |
|
| 2. |
Which
compound has the higher vapor pressure? |
|
| A) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-OH |
B) |
HO-CH2-CH2-OH |
|
| 3. |
Which
compound has the highest viscosity |
|
| A) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH |
| B) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 |
| C) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 |
|
| 4. |
Which
compound has the lowest heat of vaporization? |
|
| A) |
HO-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH |
| B) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH |
| C) |
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 |
|
| 5. |
What type of crystalline lattice does ice have?
|
|
| A) |
ionic |
D) |
atomic |
| B) |
metallic |
E) |
molecular |
| C) |
network
covalent |
|
|
|
| 6. |
What
type of crystalline lattice does NH4NO3
have? |
|
| A) |
metallic |
D) |
ionic |
| B) |
molecular |
E) |
atomic |
| C) |
network
covalent |
|
|
|
| 7. |
What
force in liquid mercury is most responsible for its
convex meniscus in a glass tube? |
|
| A) |
ionic
bonding |
D) |
covalent
bonding |
| B) |
dipole-dipole |
E) |
metallic
bonding |
| C) |
hydrogen
bonding |
F) |
London
dispersion |
|
| 8. |
The
reaction associated with the vaporization of H2O
is |
|
| A) |
H2O(l) 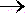 H2(g) + ½O2(g)
H2(g) + ½O2(g) |
| B) |
H2O(l)  H2O(g)
H2O(g) |
| C) |
H2O(s)  H2(g) + ½O2(g)
H2(g) + ½O2(g) |
| D) |
H2O(s)  H2O(g)
H2O(g) |
|
| 9. |
What
do "a" and "b" represent in the van
der Waals equation of state for one mole of gas?
(P + a/V2) (V-b) = RT
|
|
| A) |
a
= attractive forces between molecules; b = attractive
forces between molecules |
| B) |
a
= attractive forces between molecules; b = finite size
of molecules |
| C) |
a
= finite size of molecules; b = attractive forces
between molecules |
| D) |
a
= finite size of molecules; b = finite size of molecules |
|
| 10. |
Determine
DH
for the process
H2O(l, 25°C)  H2O(g, 100°C).
H2O(g, 100°C).
The heat of vaporization of water is 40.7
kJ/mol and the heat capacity of liquid water is 75.4 J/mol·ºC. |
|
| A) |
46.4
kJ |
D) |
35.0
kJ |
| B) |
44.5
kJ |
E) |
52.1
kJ |
| C) |
48.3
kJ |
F) |
41.8
kJ |
|
| 11. |
The
expected attractive forces between H2
molecules are:
|
|
| A) |
London
dispersion only |
| B) |
dipole-dipole
only |
| C) |
dipole-dipole
and London dispersion |
| D) |
hydrogen
bonding and London dispersion |
| E) |
hydrogen
bonding only |
| F) |
dipole-dipole
and hydrogen bonding |
|
| 12. |
The
expected attractive forces between HCl molecules are
|
|
| A) |
London
dispersion only |
| B) |
dipole-dipole only |
| C) |
dipole-dipole
and London dispersion |
| D) |
hydrogen
bonding and London dispersion |
| E) |
hydrogen
bonding only |
| F) |
dipole-dipole
and hydrogen bonding |
|
| 13. |
The
expected attractive forces between NH 3
molecules are:
|
|
| A) |
London
dispersion only |
| B) |
dipole-dipole
only |
| C) |
dipole-dipole
and London dispersion |
| D) |
hydrogen
bonding and London dispersion |
| E) |
hydrogen
bonding only |
| F) |
dipole-dipole
and hydrogen bonding |
|
| 14. |
Which
of these compounds has the highest boiling point? |
|
| A)
CH4 |
B)
CF4 |
C)
CCl4 |
D)
CBr4 |
|
| 15. |
Which
of these compounds has the lowest boiling point?
|
|
| A)
HF |
B)
HCl |
C)
HBr |
D)
HI |
|
| 16. |
If
the
phase diagram has the normal boiling point at 80°C what
is the normal freezing point? |
|
| A) |
20°C |
|
| B) |
30°C |
| C) |
40°C |
| D) |
50°C |
| E) |
60°C |
|
| 17. |
Identify
the sublimation curve from possible answers A-E on the
phase diagram.
|
|
| 18. |
What
type of crystalline lattice does CO 2 have? |
|
| A) |
metallic |
| B) |
ionic |
| C) |
network
covalent |
| D) |
atomic |
| E) |
molecular |
|
| 19. |
Which
reaction describes deposition? |
|
| A) |
CO2(s)  CO2(g), endothermic
CO2(g), endothermic |
| B) |
CO2(g)  CO2(s), exothermic
CO2(s), exothermic |
| C) |
CO2(g)  CO2(s), endothermic
CO2(s), endothermic |
| D) |
CO2(s)  CO2(g), exothermic
CO2(g), exothermic |
| E) |
CO2(l)  CO2(g), endothermic
CO2(g), endothermic |
| F) |
CO2(g)  CO2(l), exothermic
CO2(l), exothermic |
| G) |
CO2(g)  CO2(l), endothermic
CO2(l), endothermic |
| H) |
CO2(l)  CO2(g), exothermic
CO2(g), exothermic |
|
| 20. |
Predict
the intermolecular forces between molecules of CH3-O-CH3,
dimethyl ether: |
|
| A) |
London
dispersion only |
| B) |
dipole-dipole
only |
| C) |
dipole-dipole
and London dispersion |
| D) |
hydrogen
bonding and London dispersion |
| E) |
hydrogen
bonding only |
| F) |
dipole-dipole
and hydrogen bonding |
|
|
|
|